
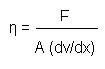

A viscometer comprises two reservoir bulbs and a capillary tube. U-tube viscometers are also known as glass capillary viscometers or Ostwald viscometers. However, an appropriate measure of viscosity can be given with the help of a viscometer. The slower the ball will fall, the greater the viscosity it will have. The primary way of measuring viscosity is to drop a sphere, such as a ball, in a fluid and simultaneously time the fall of it. Measuring the viscosity of any matter helps in determining and designing the production and transportation procedure. For example, if the viscosity of toothpaste is not appropriate it will either be very difficult to pump out the toothpaste or a lot of toothpaste will be pumped out in one go. Viscosity of a given matter is calculated in order to measure the behaviour of the matter in the actual world. Viscosity has a dimensional formula of . For instance, the viscosity of water at 27☌ (81☏) is 0.85 × 10 −3 and at 77☌ (171☏) it is 0.36 × 10 −3 pascal-second. However, the same for air at these temperatures are 1.85 × 10 −5 and 2.08 × 10 −5 pascal-second respectively.ĭifference in Viscosity between Water and Honey The SI unit of Viscosity if Poiseiulle (PI). Viscosity can be referred to as friction between the molecules of fluid. When the temperature is high the kinetic energy of a molecule also rises which results in the slipping of the intermolecular through one another between the layers. The Viscosity in a liquid decreases with the rise in temperature. The formula of Viscosity is: \(η = \frac\). The reciprocal of the viscosity is known as “fluidity”, which can be defined as a measure of the ease of flow. It typically occurs when a relative motion can be found between the layers of the fluid. Viscosity simply represents “the opposition to flow”.
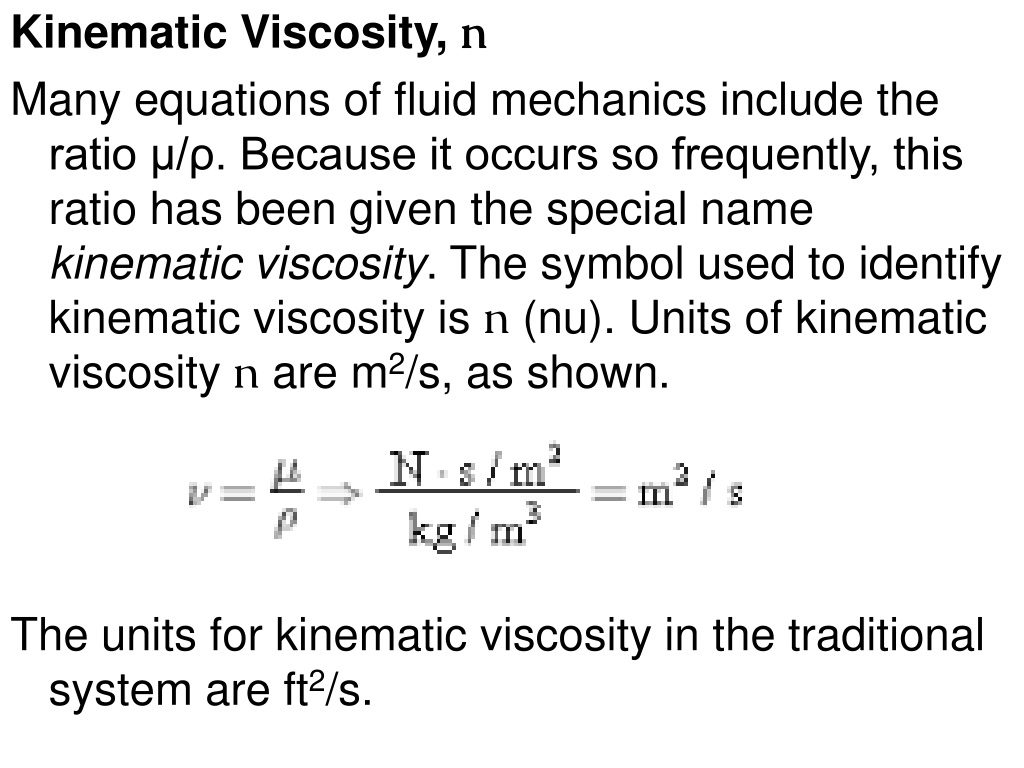
Thermal properties of water at different temperatures like density, freezing temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of melting, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more.Viscosity measures the resistance in the flow of a liquid which arises due to internal frictions between layers of the fluids. Introduction and definition of the dimensionless Reynolds Number - online calculators. Temperature and Pressureįigures and tables with Prandtl Number of liquid and gaseous propane at varying temperarure and pressure, SI and Imperial units. Temperature and Pressureįigures and tables showing Prandtl number of nitrogen at varying temperarure and pressure, SI and Imperial units. Thermodynamic properties of dry air - specific heat, ratio of specific heats, dynamic viscosity, thermal conductivity, Prandtl number, density and kinematic viscosity at temperatures ranging 175 - 1900 K.įigures and table showing changes in Prandtl number for methane with changes in temperature and pressure. Physical and chemical dimensionless quantities - Reynolds number, Euler, Nusselt, and Prandtl number - and many more.ĭry Air - Thermodynamic and Physical Properties Properties of saturated liquid Carbon Dioxide - CO 2 - density, specific heat, kinematic viscosity, thermal conductivity and Prandtl number. Temperature and Pressureįigures and table with changes in Prandtl number for ammonia with changes in temperature and pressure. Ideal gas properties of air at low pressure - SI units.Īmmonia - Prandtl Number vs. Thermodynamic properties of air at low pressures - imperial units. Involving velocity, pressure, density and temperature as functions of space and time.
#Kinematic viscosity formula and unit free
The Prandtl Number is often used in heat transfer and free and forced convection calculations. It depends on the fluid properties.Įxample - Calculation of a Prandtl Numberĭynamic viscosity can be converted from cP to lb m/(ft h) as K = thermal conductivity (W/m K, Btu/(h ft 2 oF/ft)) Μ = absolute or dynamic viscosity (kg/m s, lb m/(ft h))Ĭ p = specific heat (J/kg K, Btu/(lb m oF)) The Prandtl number can alternatively be expressed as The Prandtl Number is a dimensionless number approximating the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to thermal diffusivity - and can be expressed as


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
